~94% Accuracy While Shortening TAT to 5 Minutes: Explore Zybio MALDI-TOF MS with Advanced Rapid Blood Culture Enrichment Technology
April 16, 2025 Zybio News
-

December 26, 2025
DiagHub Online Academic Platform The ninth session on Microbiology Concludes Successfully – Highlights Recap
-

Nov 28, 2025
DiagHub Online Academic Platform The eighth session on Molecular Concludes Successfully – Highlights Recap
-

Nov 21, 2025
Zybio at MEDICA 2025: Comprehensive Laboratory Diagnostic Solution
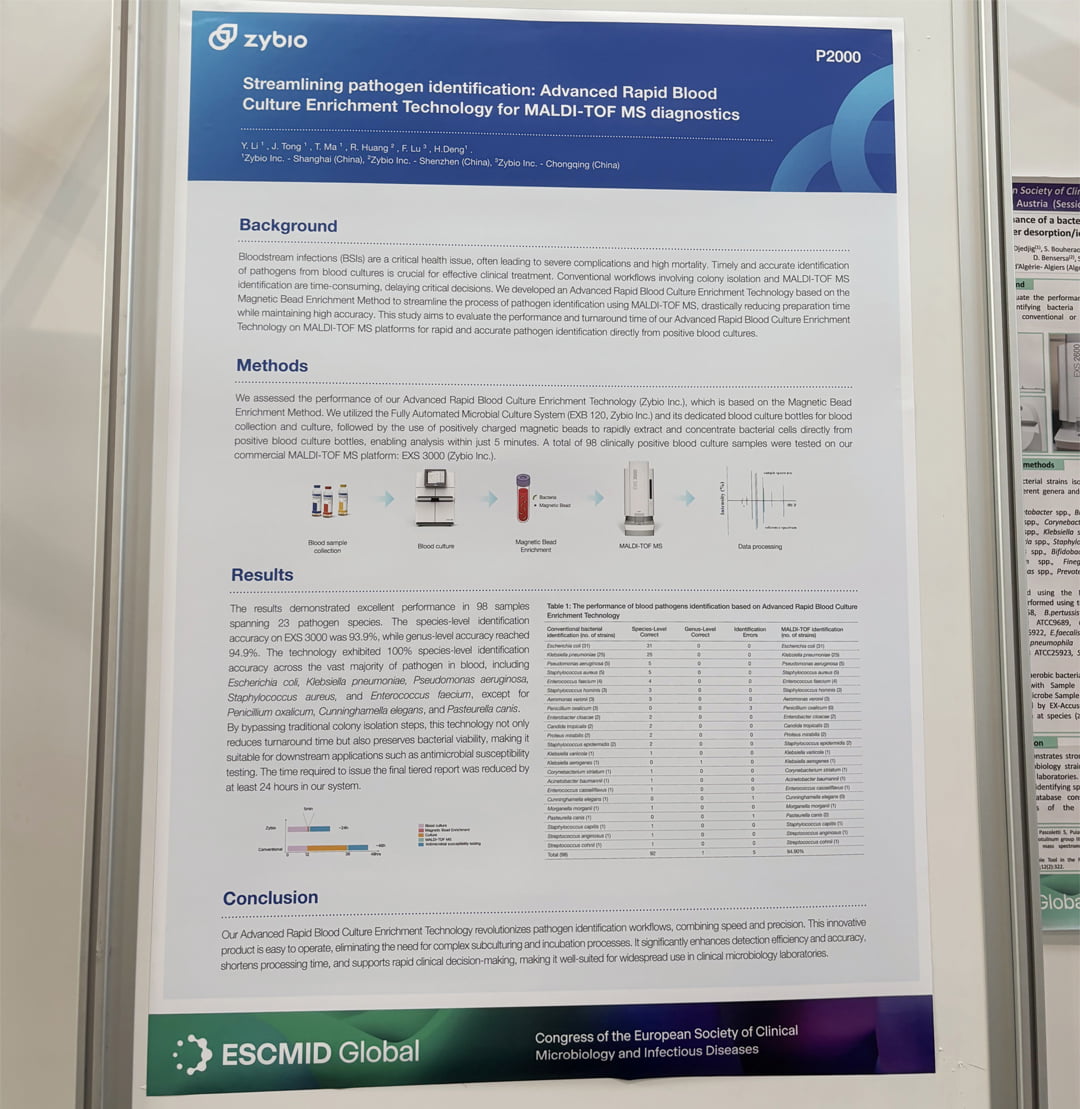
In ESCMID 2025, Zybio had 4 posters successfully accepted, which were showcased in ESCMID hall during the congress. One of them, titled “Streamlining Pathogen Identification: Advanced Rapid Blood Culture Enrichment Technology for MALDI-TOF Diagnostics”, evaluates Zybio’s advanced magnetic bead enrichment technology in accuracy and efficiency, and finds reliable accuracy more than 94% as well as greatly shortened TAT from 8 hours to 5 minutes.
Bloodstream Infection And Clinical Diagnostics
Bloodstream infections (BSIs) refer to systemic inflammatory response syndrome caused by the invasion of pathogenic microorganisms and their toxins into the bloodstream[1], which can lead to bacteremia, sepsis, and septic shock. With rising incidence due to more invasive medical procedures and antibiotic misuse, BSIs now affect approximately 150 out of every 100,000 people annually, carrying a 30-day mortality rate of 17% for detected cases with positive blood culture[2]. Notably, in cases of septic shock, each hour of delay in treatment increases mortality by 7.6%—reaching 58% within just 6 hours[3].
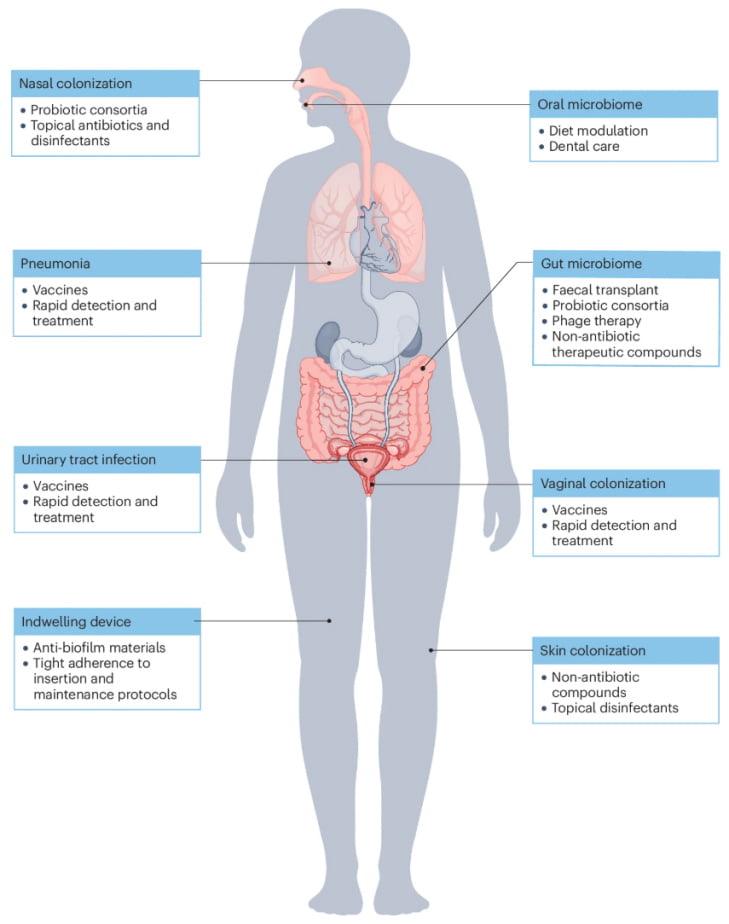
Origins of BSIs from different primary sites [4]
Blood culture remains the "gold standard" for diagnosing BSIs, as it allows pathogen isolation and antibiotic susceptibility testing (AST) [5]. However, blood culture is time-consuming and often lacks sensitivity, particularly for fastidious or slow-growing bacteria. As a result, it falls short in guiding immediate clinical decision-making. In practice, patients with suspected BSIs are typically treated empirically with broad-spectrum antibiotics, which are later refined based on culture and AST results.[6]. To address these limitations, emerging technologies, such as matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS), nucleic acid amplification, and cell-free DNA sequencing, offer rapid pathogen identification, potentially shortening antimicrobial therapy duration and limiting unnecessary antibiotic exposure to help combat antimicrobial resistance.
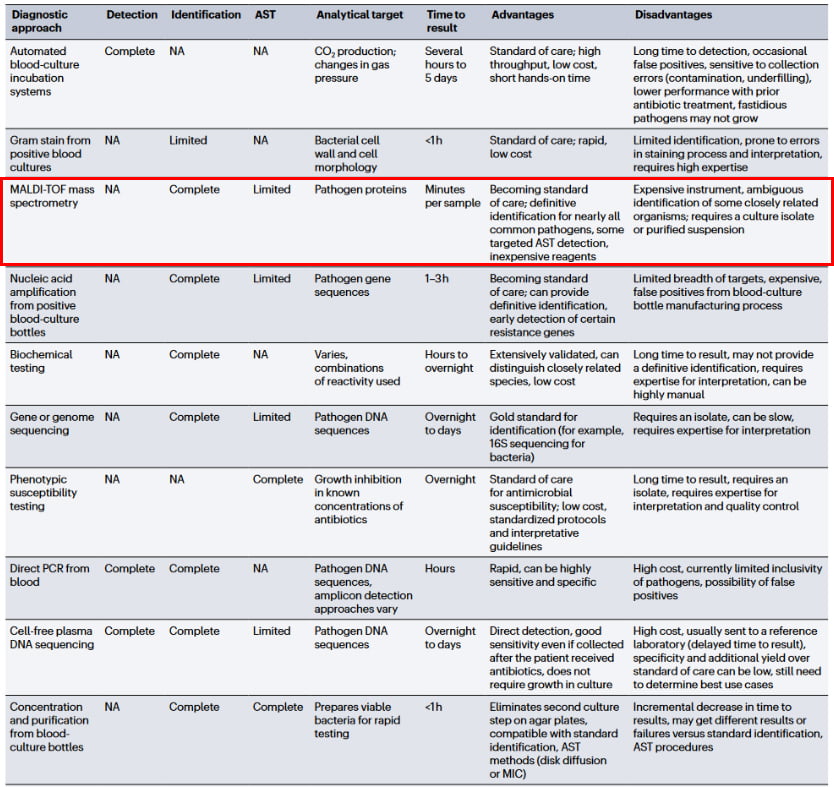
Figure 2: Comparison of BSI detection methods [4]
Zybio Employs Advanced Magnetic Bead Enrichment Technology to Facilitate Rapid Microbial Identification in Clinical BSIs
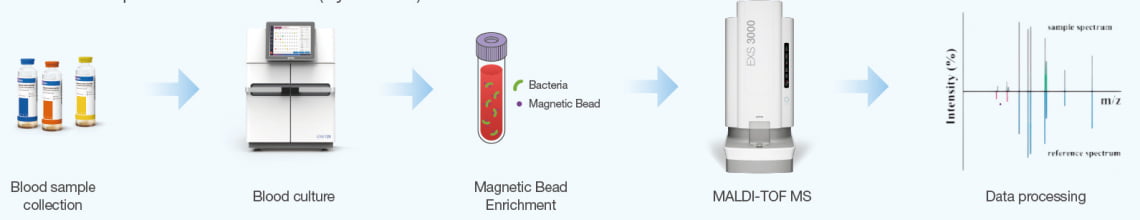
Study Highlights: Next-Generation Magnetic Bead Enrichment for Faster Diagnostics
Zybio adopts an advanced rapid blood culture enrichment technology based on magnetic bead enrichment to accelerate pathogen identification from positive blood cultures using MALDI-TOF MS. This method utilizes positively charged magnetic beads to rapidly concentrate bacteria from positive blood culture bottles, eliminating repeated centrifugation or subculture steps. The process simplifies MALDI-TOF MS pathogen identification, achieving bacterial enrichment in 5 minutes with 93.9% species-level and 94.9% genus-level detection rates, significantly reducing turnaround time while maintaining high accuracy.
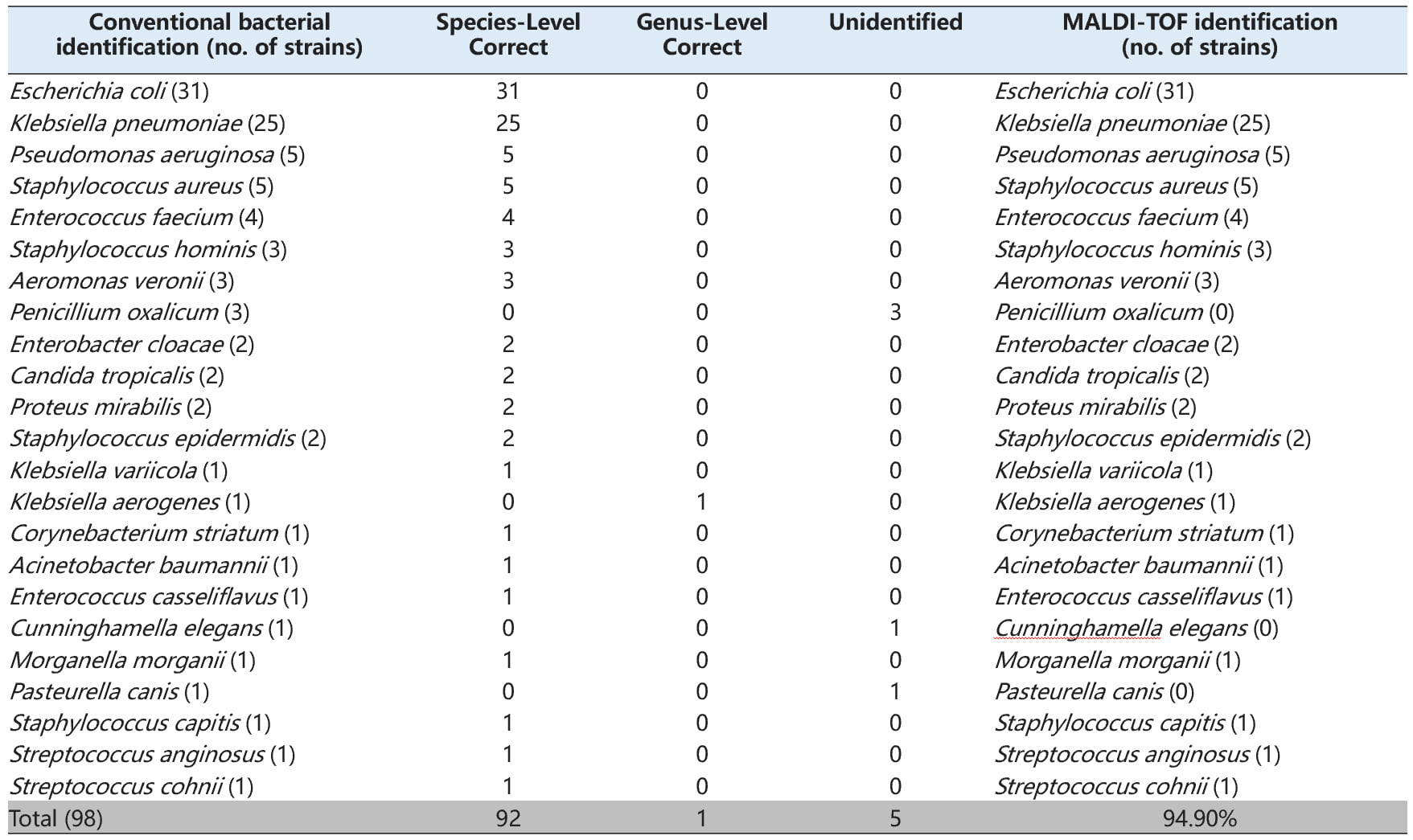
Compared to traditional colony isolation methods, this technology preserves bacterial viability for subsequent drug susceptibility testing and reduces the diagnostic cycle by at least 24 hours.
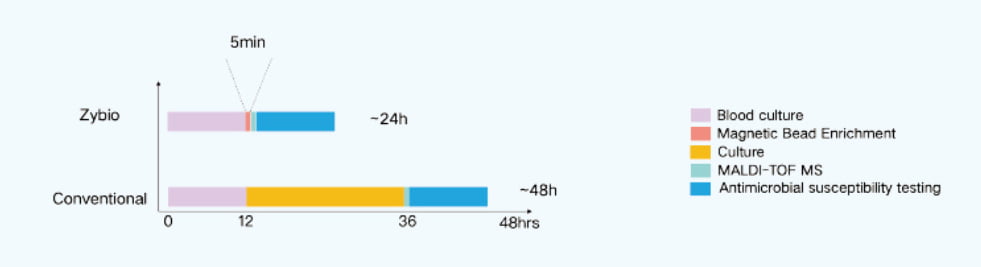
How does Zybio MALDI-TOF MS Facilitate Clinical Microbiology
This streamlined method enhances speed and precision of pathogen identification, improves patient outcomes in critical BSI cases with faster supports for clinical decision-making, and simplifies lab workflows, making it ideal fit for clinical microbiology in laboratories.
Zybio has been and will always be committed to the concept of "striving for excellence" and constantly go further in technology of laboratory testing. Meanwhile, we, with customer-centered notion in mind, will improve our services in an all-round and multi-angle manner to provide more comprehensive and efficient solutions for healthcare providers, and in this way, we safeguard patients' lives and health.
·Reference
[1] Martinez R M, Wolk D M. Bloodstream Infections[J]. Microbiology Spectrum, 2016, 4(4).
[2] Verway M, Brown K A, Marchand-Austin A, et al. Prevalence and Mortality Associated with Bloodstream Organisms: a Population-Wide Retrospective Cohort Study[J]. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 2022, 60(4): e0242921.
[3] Kumar A, Roberts D, Wood K E, et al. Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock[J]. Critical Care Medicine, 2006, 34(6): 1589-1596.
[4] Holmes C L, Albin O R, Mobley H L T, et al. Bloodstream infections: mechanisms of pathogenesis and opportunities for intervention[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2025, 23(4): 210-224.
[5] Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021[J]. Intensive Care Medicine, 2021, 47(11): 1181-1247.
[6] López-Cortés L E, Delgado-Valverde M, Moreno-Mellado E, et al. Efficacy and safety of a structured de-escalation from antipseudomonal β-lactams in bloodstream infections due to Enterobacterales (SIMPLIFY): an open-label, multicentre, randomised trial[J]. The Lancet. Infectious Diseases, 2024, 24(4): 375-385.